How Long Does Dexamethasone Affect Blood Sugar?
Dexamethasone’s duration of action on blood sugar levels can vary based on the patient, the dosage, and the length of the course of therapy. Generally speaking, using dexamethasone can result in a surge in blood sugar levels within hours, and this effect can persist for a few days or longer, even after the drug has been stopped.
Dexamethasone And Blood Sugar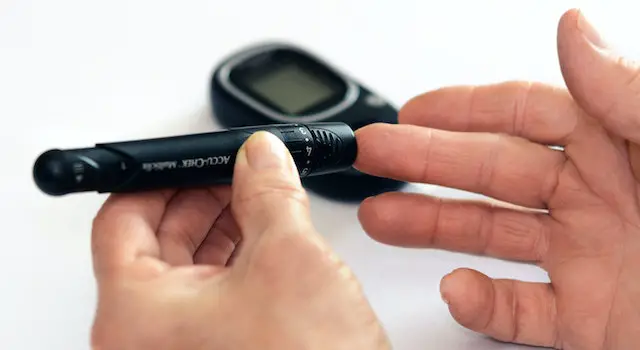
Dexamethasone is a steroid drug commonly employed to treat a range of ailments, such as inflammation, various types of cancer, and autoimmune diseases. While dexamethasone may be a successful treatment for these ailments, it also has negative side effects, like increased blood sugar levels.
How Does Dexamethasone Affect Blood Sugar?
Dexamethasone may alter the levels of blood sugar in multiple ways. It can first cause an increase in insulin resistance. This implies that the body requires more insulin to control blood sugar levels. This could result in blood sugar levels increasing. Dexamethasone is also known to increase the production of glucose in the liver. This could cause blood sugar levels to increase. Additionally, dexamethasone could reduce glucose absorption in muscles, which could cause high blood sugar levels.
For those who suffer from the disease or are at risk of developing it, the effects of dexamethasone could be particularly challenging. People who suffer from diabetes already struggle to regulate blood sugar levels. The extra insulin resistance and the glucose production caused by dexamethasone could make it more difficult to keep blood sugar levels in a normal range.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels While Taking Dexamethasone
Suppose you’re on dexamethasone and suffer from diabetes or have a high risk of developing it. In that case, it is crucial to check your blood sugar levels frequently and collaborate closely with your healthcare professional to monitor the changes in your blood sugar levels. Your healthcare provider might suggest adjustments to your insulin or diabetes medication dosage when you’re taking dexamethasone to keep your blood sugar levels under control.
As well as monitoring blood sugar levels and changing dosages, there are additional ways to control blood sugar levels when taking dexamethasone. These include:
- A healthy diet is low in carbohydrates and sugar. This can help reduce blood sugar spikes and decrease the need for insulin.
- Engaging in regular physical exercise. Exercise can increase insulin sensitivity and control blood sugar levels.
- Sleeping enough. Lack of sleep can affect the metabolism of glucose, causing blood sugar levels to increase.
- Avoiding tobacco and alcohol Both tobacco and alcohol can raise blood sugar levels, making it harder to control diabetes.
Duration Of Dexamethasone’s Effect On Blood Sugar
One of the consequences of dexamethasone is that it can increase blood sugar levels. This could be a problem for those suffering from diabetes or at risk of developing diabetes.
How Long Does Dexamethasone Affect Blood Sugar?
The duration of dexamethasone effect on blood sugar levels may differ based on various factors, including the person’s dosage, the individual, and the length of treatment. Dexamethasone may cause a rise in blood sugar levels as early as a few hours after taking the medication, and this effect may last for a few days or more, even after treatment has been stopped.
One study showed that dexamethasone triggered blood sugar levels to rise within 24 hours after taking the medication, and the effect lasted for as long as 72 hours. Another study revealed that dexamethasone led to blood sugar levels rising within six hours after taking the medication and that this effect lasted up to four days.
It is important to remember that dexamethasone’s effects on blood sugar levels may depend on the dose of the drug. More dexamethasone doses could cause a more dramatic rise in blood sugar levels and may have a longer-lasting impact on blood sugar levels.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels While Taking Dexamethasone
Suppose you’re taking dexamethasone and suffer from diabetes or have a high risk of developing it. In that case, it is crucial to check your blood sugar levels frequently and closely work with your healthcare professional to monitor any fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Your healthcare provider might suggest modifications to your insulin or diabetes medication dosage when you’re taking dexamethasone to keep your blood sugar levels under control.
In addition to observing blood sugar levels and making adjustments to dosages, there are additional actions you can take to control blood sugar levels when taking dexamethasone. These include:
- Consuming a balanced diet that is low in carbohydrates and sugars This can help reduce blood sugar spikes and the requirement for insulin.
- Regularly exercising. Exercise can increase insulin sensitivity and control blood sugar levels.
- Insufficient sleep. Lack of sleep can affect the metabolism of glucose and cause blood sugar levels to increase.
- Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol. Both tobacco and alcohol can raise blood sugar levels, making it harder to manage diabetes.
Management Of Dexamethasone-Induced Hyperglycemia
Dexamethasone is a potent corticosteroid medication because of its anti-inflammatory and immune-suppressive properties. It can be used to treat a range of conditions, such as inflammation, allergies, and autoimmune disorders. However, one of the side effects of dexamethasone can be hyperglycemia, which is high blood sugar. This can be especially problematic for those who are already diabetic or are at risk of developing diabetes.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
The first step in managing dexamethasone-induced hyperglycemia is regularly monitoring blood sugar levels. This is especially important for people who have diabetes or a history of excessive blood sugar levels. The blood sugar levels can be checked by using a blood glucose meter, a tiny device that measures the amount of sugar in the blood. It is recommended that people test their blood sugar levels at least four times per day, including before meals and before bedtime.
If your blood sugar levels remain high, adjusting medications or insulin doses could be necessary. In certain instances, healthcare professionals might recommend starting a brand new medication or altering the dosage of an existing drug to lower blood sugar levels. Collaborating with a healthcare doctor to create a customized plan to monitor blood sugar levels and prevent hyperglycemia is essential.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to monitoring blood sugar levels, lifestyle changes can help manage dexamethasone-induced hyperglycemia. Some of these changes could include:
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Healthy eating can regulate blood sugar levels and improve general health. Maintaining a balanced diet that includes vegetables, fruits, protein, lean proteins, and whole grains is crucial. Avoiding processed and sugary foods may also help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Regularly engaging in physical exercise will increase insulin sensitivity and control blood sugar levels. You are advised to take at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise every week.
- Maintaining an appropriate weight Obesity can cause an increase in insulin resistance and also increase the chance of developing hyperglycemia. A healthy weight achieved through exercise and diet can help control blood sugar levels.
Medications
In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage dexamethasone-induced hyperglycemia. Some of the drugs that can be prescribed include:
- Insulin: Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Patients with diabetes may need to begin taking insulin to control blood sugar levels while taking dexamethasone.
- The oral hypoglycemic agent: These medications aid in regulating blood sugar levels by enhancing insulin sensitivity or reducing glucose production within the liver.
- GLP-1 agonists: These medications aid in regulating blood sugar levels by stimulating insulin release and reducing glucose production by the liver.
Working closely with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate medication and dosage for managing dexamethasone-induced hyperglycemia is important.
In addition to traditional medications, some alternative treatments may effectively manage dexamethasone-induced hyperglycemia. The treatments are:
- Herbal supplements: Certain herbal supplements, including cinnamon, the ginseng plant, and fenugreek, have been proven to increase insulin sensitivity and control blood sugar levels.
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture could aid in regulating blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of endorphins and other hormones that regulate metabolism.
- Meditation and yoga: These practices can aid in controlling blood sugar levels, lower stress levels, and promote relaxation.
Precautions And Risks
The corticosteroid dexamethasone can be a powerful drug prescribed to treat a range of ailments, including inflammation, allergies, and autoimmune diseases. Although it’s usually safe and efficient, some precautions and risks come with dexamethasone’s use.
Precautions
Before taking dexamethasone, discussing any medical condition or medication with a physician is crucial. Dexamethasone can interfere with some medications or worsen existing medical conditions, like hypertension or diabetes. It is crucial to inform your doctor of any previous history of these ailments.
Dexamethasone must also be taken cautiously by those with an established history of gastrointestinal bleeding or ulcers. The medication may increase the chance of developing ulcers or bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, particularly if used for long durations. People with a history of gastrointestinal bleeding or ulcers should discuss other treatments with a medical doctor.
Dexamethasone can also suppress the immune system. This could make me more likely to get sick. It is essential to maintain proper hygiene and stay away from contact with those who are sick when taking dexamethasone. In certain instances, a doctor may suggest a prophylactic antibiotic to decrease the infection risk.
Risks
One of the most significant dangers associated with dexamethasone usage is hyperglycemia, an abnormally high blood sugar level. This can be particularly challenging for people who already have diabetes or are at risk of developing it. It is essential to monitor blood sugar levels frequently when taking dexamethasone and to collaborate with a medical professional to treat hyperglycemia if it occurs.
Dexamethasone may also cause weight gain and fluid retention, particularly when used for long durations. This could increase the chance of developing congestive heart failure or hypertension. It is essential to check blood pressure and weight frequently when taking dexamethasone and collaborate closely with a medical professional to address potential issues.
Long-term use of dexamethasone may also increase the chance of developing osteoporosis. It is a condition that manifests as weak bones. This could increase the chance of fractures and other complications. Patients taking dexamethasone for long durations should discuss ways of treating or preventing osteoporosis with a doctor.
Withdrawal and Dependence
Dexamethasone shouldn’t be stopped abruptly, as it could cause withdrawal symptoms like muscle weakness, fatigue, and joint pain. In some instances, the doctor might suggest gradually tapering the dosage of dexamethasone to reduce the chance of experiencing withdrawal symptoms.
The long-term use of dexamethasone may result in dependence. The body gets used to the drug and needs it to perform normally. Dependency can make quitting the drug difficult, even when it’s not required anymore. Collaborating with a medical doctor to create a plan to manage dependence and stop the medication when appropriate is essential.
Clinical Uses Of Dexamethasone And Blood Sugar Control

Dexamethasone is an artificial corticosteroid medication widely employed in clinical practice because of its powerful anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. One of the possible The adverse effect of dexamethasone is its effect on blood sugar levels. This can be particularly detrimental for people who suffer from diabetes or are at risk of developing diabetes.
Clinical Uses of Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone can treat many conditions, such as allergies, inflammatory disorders, and autoimmune diseases. The drug is also employed in cancer treatment to decrease swelling and inflammation caused by tumors and to aid in managing symptoms like fatigue and pain.
Dexamethasone can also treat respiratory ailments like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It may help decrease inflammation of the airways, making breathing easier. Dexamethasone is also used to treat neurological disorders like meningitis and multiple sclerosis by reducing spinal cord and brain inflammation.
Additionally, dexamethasone treats certain endocrine disorders, such as adrenal insufficiency and congenital adrenal hyperplasia. It can replace or enhance cortisol production in the body, which is crucial to regulating blood sugar levels, among other things.
Impact on Blood Sugar Control
Dexamethasone may significantly control blood sugar levels, especially when used for long durations or in large doses. This is because dexamethasone may increase insulin resistance, which means that the cells of the body are less sensitive to the actions of insulin. This can result in increased levels of blood sugar, which could be particularly challenging for people with diabetes or who are at risk of developing diabetes.
In certain cases, dexamethasone may cause the onset of diabetes in people at risk of developing the condition. This is especially relevant for those with a history of diabetes in their family or who suffer from other risk factors like being overweight or having a sedentary lifestyle.
It is crucial to monitor blood sugar levels frequently while taking dexamethasone. This is especially important when taking a prolonged or large dose. In certain instances, medical professionals may suggest adjusting diabetes medication or insulin dosages to maintain optimum blood sugar control.
Management of Hyperglycemia
If you do experience hyperglycemia when taking dexamethasone, many strategies for managing it can be utilized. In some instances, adjusting the dosage of dexamethasone or switching to a different medication can help lower the blood sugar level. In other instances, the insulin or diabetes medication might need to be adjusted to help manage hyperglycemia.
It is also essential to implement lifestyle changes to manage blood sugar levels, for example, eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and monitoring blood sugar levels regularly. In certain instances, the healthcare professional might suggest working with an experienced registered dietitian or diabetes educator to design an individual plan for managing blood sugar levels when taking dexamethasone.
Alternative Steroid Medications And Blood Sugar Control
Steroids are a class of medications typically employed in treating chronic autoimmune and inflammatory conditions. However, certain steroids, like dexamethasone, can have a significant effect on blood sugar levels and are therefore not suitable for those suffering from diabetes or who are at risk of developing diabetes.
Alternative Steroid Medications
One alternative to dexamethasone is prednisone, which is an identical corticosteroid medication. Prednisone can also treat a range of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders and reduce swelling and inflammation. While it can raise blood sugar levels, it’s generally less effective than dexamethasone and could be a better choice for those at risk of developing diabetes.
An alternative to dexamethasone is hydrocortisone, which is a corticosteroid that naturally occurs and is created by the adrenal gland. Hydrocortisone treats many ailments, including inflammation and autoimmune diseases, and can reduce swelling and inflammation. Although hydrocortisone may also raise blood sugar levels, it’s generally less effective than dexamethasone. It could be a better choice for those at risk of developing diabetes.
Additionally, some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen could be used instead of steroids to treat certain inflammatory conditions. While NSAIDs don’t have the same effect on blood sugar levels, they could cause other negative effects, like stomach irritation and an increased risk of cardiovascular events.
impact on blood sugar control
Although other steroid medications might be less effective than dexamethasone, they can affect the control of blood sugar. Hydrocortisone and prednisone, for instance, can cause an increase in insulin resistance, which can result in increased blood sugar levels, especially when used for prolonged durations or in large doses.
It is essential to check blood sugar levels frequently while using steroid medications and cooperate with a medical professional to address any potential issues. In some instances, it may be necessary to adjust doses of insulin or diabetes medications to ensure the best blood sugar control.
Management of Hyperglycemia
If you experience hyperglycemia when taking an alternative medication for steroids, a variety of treatment strategies can be used. In certain instances, changing the dose of the medication or changing it to another medication could aid in reducing the blood sugar level. In other instances, the insulin or diabetes medication could require adjustments to help manage hyperglycemia.
Additionally, lifestyle changes can help control blood sugar levels, like eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and observing blood sugar levels regularly. Working with a registered dietitian or a certified diabetes educator to create an individual plan to manage blood sugar levels could be beneficial.
FAQ’s
How quickly does dexamethasone affect blood sugar levels?
Dexamethasone can affect blood sugar levels within hours of taking the medication. In some cases, blood sugar levels may rise significantly within the first day of treatment.
How long does dexamethasone stay in your system?
Dexamethasone has a half-life of about 36 to 54 hours, which means it takes this amount of time for half of the drug to be eliminated from your body. However, the effects of dexamethasone on blood sugar levels can last longer than this, depending on the individual and the dosage.
Does dexamethasone raise blood sugar permanently?
No, dexamethasone does not permanently raise blood sugar levels. The effects of the medication on blood sugar levels are temporary and will subside once the medication is discontinued.
Can dexamethasone cause diabetes?
Dexamethasone does not cause diabetes, but it can worsen existing diabetes or increase the risk of developing diabetes in people who are predisposed to the condition.
How long does it take for blood sugar levels to return to normal after stopping dexamethasone?
It can take several days to weeks for blood sugar levels to return to normal after stopping dexamethasone. This can vary depending on the individual and the dosage of the medication.
Can dexamethasone affect blood sugar levels in people without diabetes?
Yes, dexamethasone can affect blood sugar levels in people without diabetes. However, the effect is usually temporary and mild, and blood sugar levels typically return to normal once the medication is discontinued.


















